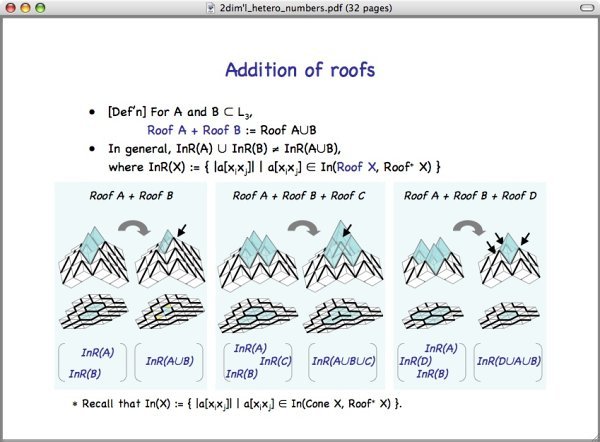
Then, addition of roofs is defined as follows.
For subset A and B of standard lattice L3, Roof A + Roof B is …
As shown below, in general, InR(A)UInR(B) is not equal to InR(AUB), where InR(X) is the projection of In(Roof X, XRoof* X) on the hyperplane.
Shown on the left is addition of two roofs Roof A and Roof B, where closed trajectories In(A) and In(B) break upon addition. The black arrow indicates the cube put on to obtain the roof.
Shown in the middle is addition of three roofs Roof A, Roof B and Cone C, where closed trajectories In(A) , In(B), and In(C) fuse into a single closed trajectory In(AUBUC) upon addition.
Shown on the right is addition of another triplet of roofs Roof A, Roof B and Cone D, where closed trajectories In(A) , In(B), and In(C) collapse into a shorter closed trajectory In(AUBUD) upon addition.
Addition of conjugate roofs is also defined similarly.