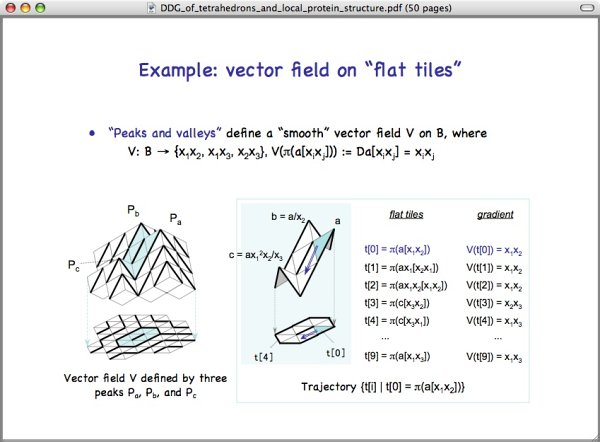
This is an example of vector field on flat tiles.
"Peaks and valleys" ...,
where vector field V is a function from B to the set of gradients and flat tile pi(a[xixj]) assumes the gradient Da[xixj] of the corresponding slant tile a[xixj] on the surface.
Shown on the left is an example of vector field V defined by three peaks. The value of V on the closed trajectory of blue tiles is shown on the right.
Let's start from flat tile t[0] colored blue and move downward. t[0] is the image of the blue slant tile a[x1x2] by pi. And the value of V on t[0] is x1x2 as shown in blue. Then, it specifies a local flow of t[9], t[0], and t[1]. Since we move downward, our next tile is t[1] and it is the image of slant tile ax1[x2x1]. Thus, the value of V on t[1] is also x1x2.
Continueing the process, we obtain the closed trajectory of length 10. And it satisfies the smoothness condition as you see.