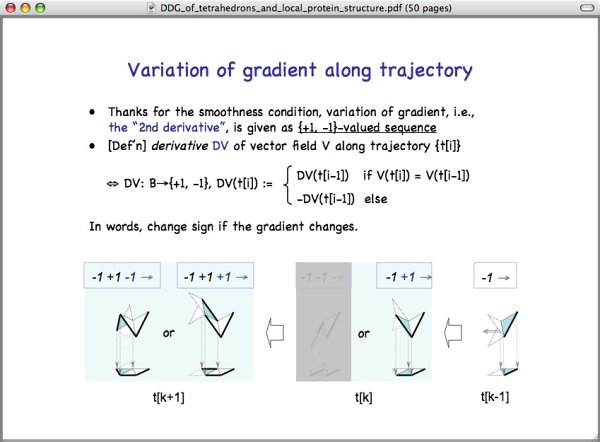
Let's choose the right case and continue the process.
The left figure shows the next tile t[k+1] (colored blue). Again, because of the smoothness condition, t[k+1] could assume one of the two blue slant tiles.
In the left case, the gradient of the "blue" next slant tile is not equal to the gradient of the "white" current slant tile. And the value of DV is changed from +1 to -1. On the other hand, in the right case, the gradient of the "blue" slant tile is equal to the gradient of the "white" slant tile. Thus, the value of DV on t[k] is +1.
In either case, we obtain a binary valued sequence of length three, which describes variation of gradient along the trajectory.