PURPOSE: Because the orthoganal coordinates of PDB files
have only three decimal places, floating point arithmetic
programs may produce
inconsistent results due to precision error after
coordinate transformation. For example,
superimposed RMSD between a PDB file and a coordinate file of its
rotated image
is no longer
0.0Angstrom.
Here we examine the robustness of the
ProteinEncoder
program.
METHOD:
First, rotate a HIV-1 PR monomer (2nph, chain A) arbitrarily and create
a
coordinate file. Next, compute superimposition of other HIV-1
PR monomers on the rotated monomer (2nphA) and create their coordinate
files, using the
DaliLite
server. Then, the
D2 code of a chain is
computed from both of the coordinate files, and the results
are compared with each other.
RESULT:
The
D2 code
is 99.9% consistent as shown below.
| Class |
|
#residues
(%) |
| residues with different D2
codes |
|
4
(0.1%)* |
| residues with the same D2
code |
|
7530
(99.9%) |
- PDB files: 1hpsA Res35 (D2 code: "R"/"3"),
1a8gA Res24 ("0"/"3"),
1zlfB Res24 ("0"/"R"), 2nphA Res69 ("G"/"0")
See
more ...
PURPOSE: We examine
how the
D2 code
can detect the subtle structural differences between two almost
identical amino acid chains.
METHOD:
HIV-1 protease (PR) is a homodimeric molecule, consisted of two
identical 99-residue polypeptide chains. The structures of the two
monomers are almost identical and superimposed RSMDs
between them are
0.1-0.6
Angstrom
for P61 crystals and
0.5-1.2
Angstrom for NMR models. We compare the
D2 codes of
the two monomers of a HIV-1 PR with each other. We also compare the
DSSP state sequences
of the
two monomers with each other.
RESULT: The
D2 code is as
sensitive as the
DSSP
state and we have successfully identified the structural
differences between the two monomers of the same HIV-1
PR molecules by comparing their
D2
codes. A total of 284
D2 code assignment
conflicts are
detected, seven of which are related to a pair of visually
indistinguishable local structures (false positive). There seems to be
a linear correlation between number of
D2 code assignment
conflicts and the
Z-Score.
As for the DSSP state, a total of
323
DSSP state assignment conflicts were observed but the
DSSP state has
no
clear relationship with the
Z-Score.
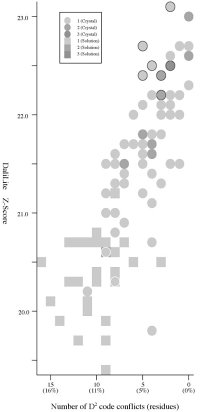
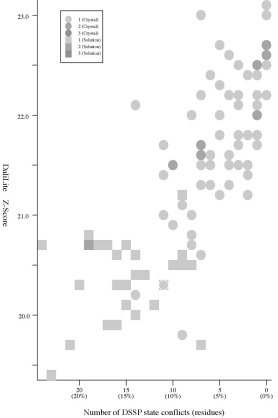
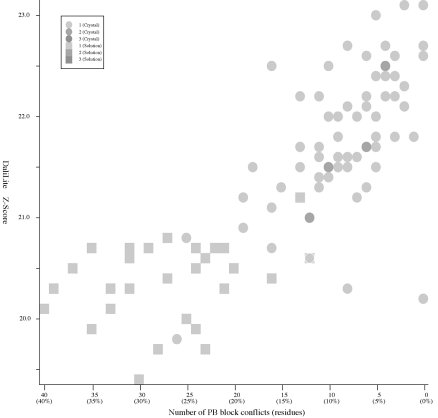
Frequency distributions of the (#{D2 code conflicts}, Z score)
value, the (#{DSSP state conflicts}, Z score) value,
and the
(#{PB block conflicts}, Z score) value of 94 pairs of
HIV-1 PR monomers:
| #{D2
code conflicts} vs Z score |
|
#{DSSP
state conflicts} vs Z score |
|
#{PB
block conflicts} vs Z score (Added 2009-04-19) |
 |
|
 |
|
|
- The Z score
is a measure of quality of
the alignment. As a general rule, above 20 means the two
structures are
definitely homologous, between 8 and 20 means the two are
probably
homologous, between 2 and 8 is a grey area, and a Z-Score below 2 is
not significant.
- Seven of the D2 conflicts are related to a
pair of visually indistinguishable local structures. Seven spheres
encircled by a black line in the left figure indicate the
position of
the HIV-1 PR dimers which contains the
conflicts. (The robustness problem.)
- Crystal:
structures of 66
P61 crystals, Solution:
structures of 28 NMR models. (See the figures)
- PB
block assignments are computed by the PBE-T server (http://bioinformatics.univ-reunion.fr/PBE/PBT.htm).
- PB
blocks are a set of 16 short structural motifs of length five
residues. See Protein Blocks Expert Home (http://bioinformatics.univ-reunion.fr/PBE)
for more info.
See
more ...
See also
EXAMPLES
(Prediction/Alignment/Others) > Structural alignment >
HIV-1 PR variants.
PURPOSE: We examine how the
D2 code-based search
can isolate structurally similar amino acid fragments from a
large
dataset.
METHOD:
Using the
ComSubstruct program,
we searched the
ASTRAL
(1.73 95%)
dataset for structurally similar amino acid
fragments of three query chains:
2nphA
(alpha+beta type, HIV-1 PR monomer),
d2hkja1 (mainly
alpha type),
and
d1j7ma_
(mainly beta type).
d2hkja1 and
d1j7ma_ are members
of the
ASTRAL (1.73
95%)
dataset. Top 200
D2 code-similar
fragments of the
same length as the query chain are obtained by typing the
following command
*:
%
ComSubstruct
-l -o1 -s -w1.0 -b200
query_chain.code target_ASTRAL173.code
Because some of the top 200 fragments overlap each
other, we chose manually a fragment for each chain contained in the top
200 (or 150) list and we
obtain 50 fragments for
2nphA (top 200),
42 fragments for
d2hkja1
(top 200),
and 55 fragments for
d1j7ma_
(top 150).
Then we used the
DaliLite
server to compute rigid structural alignment of a query chain
and each of the 50, 42 or 55 fragments. We also computed flexible
structural alignment of the pairs with the
FATCAT server.
*) The "target_ASTRAL173.code"
file (6.2MB) is available from PROGRAM>ComSubstruct>DOWNLOADS.
RESULT: We
have successfully isolated structurally similar fragments within a few
minutes on a notebook computer (2GHz
Intel Core 2 Duo
and 1GB 667MHz
DDR2 SDRAM). If the
D2 code-LCS ratio
is greater than 85%, a pair of amino acid fragments are
structurally similar. If the
D2 code-LCS ratio
is greater than 80%, a pair of amino acid fragments may be
structurally similar.
- D2
code-LCS ratio
:= length of D2 code-LCS / (the length of the
shorter chain - 4),
where LCS
stands for Longest Common Subsequence between the query chain and a
chain in the dataset.
Because two residues at the both termini of a chain are not assigned a D2
code, they are excluded from the computation. For example, there are 19
chains in the ASTRAL dataset, whose D2
code have a D2
code-LCS ratio more than or equal to 0.9 with respect to the
D2
code of 2nphA.
(a) ASTRAL dataset search by
ComSubstruct
Frequency distributions
of the length of D2 code-LCS between a query
chain
and a fragment of the same length contained in the dataset:
| D2 code-LCS
ratio |
|
2nph
A
(alpha+beta,
99 residues) |
|
d2hkja1

(mainly alpha,
78 residues) |
|
d1j7ma_
(mainly beta,
60 residues) |
[0.9,
1.0]
|
|
19
|
|
1
|
|
1
|
[0.8,
0.9)
|
|
8707
|
|
28 |
|
1713
|
[0.7,
0.8)
|
|
142703
|
|
52979 |
|
200570
|
[0.6,
0.7)
|
|
202720
|
|
542337 |
|
337648
|
[0.5,
0.6)
|
|
330742
|
|
527645 |
|
404777
|
[0.4,
0.5)
|
|
345682
|
|
239150 |
|
336195
|
[0.3,
0.4)
|
|
138008
|
|
121770 |
|
237459
|
[0.2,
0.3)
|
|
107799
|
|
19119 |
|
123953
|
[0.1,
0.2)
|
|
43223
|
|
14836 |
|
77832
|
[0.0,
0.1)
|
|
13462
|
|
927 |
|
8028
|
Total
|
|
1333065
|
|
1518792 |
|
1728176
|
- 2nphA,
d2hkja1, and d1j7ma_ are aligned with all the fragments of 99, 78, and
60 residues contained in the dataset, respectively.
(b) Length of D2
code LCS vs Z score (rigid
structural
alignment)
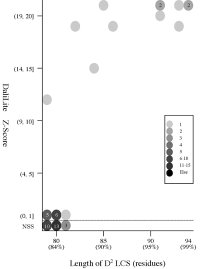
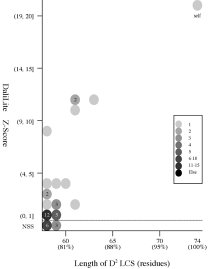
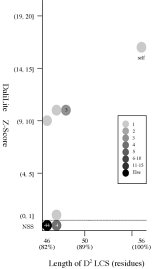
Frequency distributions
of the (length of D2 code LCS, Z score) value of 50, 42, or 55 pairs of amio
acid fragments:
2nphA
vs
50 fragments of 99 res. |
|
d2hkja1
vs
42 fragments of 78 res. |
|
d1j7ma_
vs
55 fragments of 60 res. |
|
|
|
|
|
- The Z score
is a measure of quality of
the alignment. As a general rule, above 20 means the two
structures are
definitely homologous, between 8 and 20 means the two are
probably
homologous, between 2 and 8 is a grey area, and a Z-Score below 2 is
not significant.
(c) Length of D2
code-LCS vs
P value (flexible
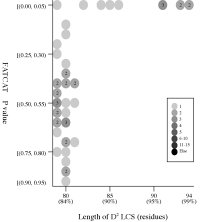
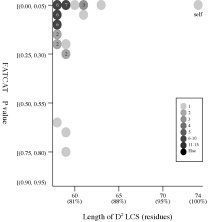
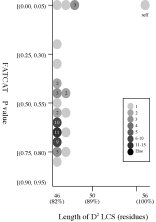
structural alignment)
Frequency distributions
of the (length of D2 code-LCS, P value) value of 50, 42, or 55 pairs of amino
acid fragments:
2nphA
vs
50 fragments of 99 res. |
|
d2hkja1
vs
42 fragments of 78 res. |
|
d1j7ma_
vs
55 fragments of 60 res. |
|
|
|
|
|
- The P value
is used in FATCAT
to evaluate the significance of structural
similarity detected by FATCAT,
the probability of observing a greater
score. Structure
pairs with P-value < 0.05 are significantly similar.
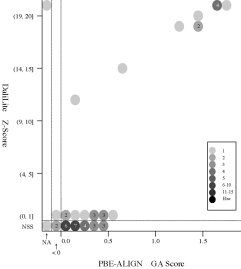
(d) [FOR REFERENCE] PBE-ALIGN global alignment (GA)
score vs Z score (Added 2009-04-19)
Frequency distributions
of the (PBE-ALIGN GA score, Z score) value of 50, 42, or 55 pairs of amino
acid fragments:
2nphA
vs
50 fragments of 99 res. |
|
d2hkja1
vs
42 fragments of 78 res. |
|
d1j7ma_
vs
55 fragments of 60 res. |
|
|
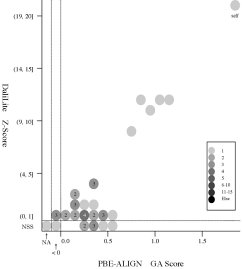
|
|
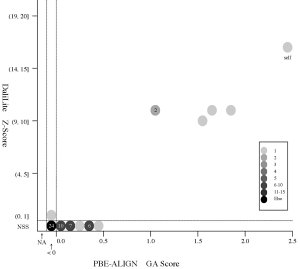
|
PURPOSE: It is widely accepted that knowledge of protein
flexibility is fundamental for understanding the mechanism of protein
function. We identify regions of 60 multiple-structure proteins
identified by Kosloff and Kolodny where conformational changes take
place.
METHOD:
We compare the
D2 codes of
two structures of the same proteins with each other. We also compare
the DSSP state sequences of the
two structures with each other. Moreover, we compute rigid and flexible
structural alignment of the two structures of the same proteins, using
the
DaliLite
and the
FATCAT
server.
RESULT: Due
to the sensitivity of the
D2 code to the
twisting of a protein backbone, the
sources of structural differences are successfully pinpointed by
comparison of
D2 codes. All the
pairs with a
DaliLite
Z-Score above eight but one have a
D2 code-LCS
ratio above 80%, although there is no clear correspondence
between the
Z-Score
and the length of
D2
code-LCS. The plot of the two values (See (a) left) shows
that large
structural
differences are often caused by deformation on small regions of a
protein, such as hinge motions.
(a) Frequency distributions
Frequency distributions
of the (length of D2 code-LCS, Z-Score) value
and
the
(length of D2 code-LCS, P-value) value of 60 structure pairs of
multiple-structure proteins:
| Length
of D2 LCS vs Z-Score |
|
Length
of D2 LCS vs P-value |
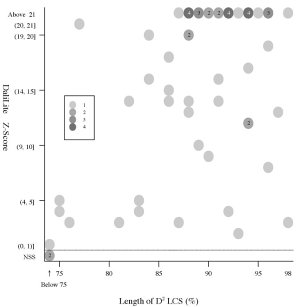 |
|
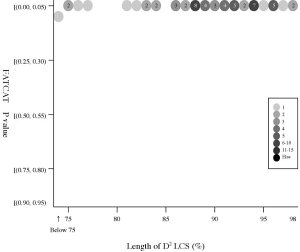 |
- The Z-Score
is a measure of quality of
the alignment. As a general rule, above 20 means the two
structures are
definitely homologous, between 8 and 20 means the two are
probably
homologous, between 2 and 8 is a grey area, and a Z-Score below 2 is
not significant.
- The P-value
is used in FATCAT
to evaluate the significance of structural
similarity detected by FATCAT,
the probability of observing a greater
score. Structure
pairs with P-value < 0.05 are significantly similar.
- All but the 1sfcD/1xtgB
pair have P-value less than 0.05.
(b) Average lengths of D2
code/DSSP state -variable
regions
D2
code-variable regions
|
|
#{residues
with
variable D2 code} |
|
Ave.
length (residues) |
|
|
Rigid span |
Variable
span |
| HIV-1 PR monomers (66 P61 crystals) |
|
4.5% |
|
25.1
res. |
1.2
res. |
| HIV-1 PR monomers (28 NMR models) |
|
10.6%
|
|
11.3
res. |
1.4
res. |
| 60 structure-dissimlar pairs |
|
12.1% |
|
14.4
res. |
2.0
res. |
- Multiple-structure proteins can be
thermodynamically identified with a sequence of D2-rigid subdomains of
an average length 14.4
residues
connected by D2-variable regions of an average length 2.0 residues.
DSSP
state-variable regions
|
|
#{residues
with
variable DSSP state} |
|
Ave.
length (residues) |
|
|
Rigid span |
Variable
span |
| HIV-1 PR monomers (66 P61 crystals) |
|
4.9% |
|
33.2
res. |
1.7
res. |
| HIV-1 PR monomers (28 NMR models) |
|
15.2%
|
|
12.6
res. |
2.3
res. |
| 60 structure-dissimlar pairs |
|
13.0% |
|
16.3
res. |
2.5
res. |
- Concerning the DSSP state, solution structure (15.2%) is
more flexible than multiple-structure
proteins (13.0%).
(c) Average alignment lengths of 60
structure-dissimilar pairs
| Programs |
|
Number
of aligned residues
(%) |
| DaliLite (rigid struct'l alignment) |
|
170.82
(80.6%) |
| ComSubstruct (D2
code alignment) |
|
187.31
(90.1%*) |
| FATCAT (flexible struct'l alignment) |
|
205.72
(97.1%) |
|
|
|
| Ave. length of the proteins |
|
211.85
(100%) |
*) Two residues at the both termini of a protein
are
excluded from the computation because they are not assigned a D2 code: 0.901=187.31/(211.85
- 4).
Frequency distributions in the ASTRAL dataset
Frequency
of occurrence of
the DSSP states / D2 codes / PB fragments among 9 superfolds
(1thbA, 256bA, 1aps, 1ubq, 2fox, 7timA, 1ilb, 2buk, and 2rhe)
*See also the page of
"Superfolds2."
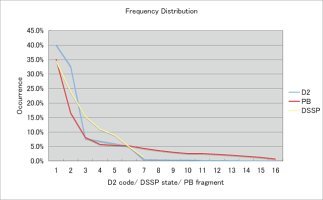 |
Frequency of occurrence of the
DSSP state / D2 code / PB fragments among 9 superfolds
|
*There are
seven DSSP
states,
16 D
2 codes, and
16 PB fragments
.
*Although there are 16 D2 codes, seven
of them already cover 98.3% of all the residues of the 9
superfolds.

















